|
How Does A
Helicopter Fly?
A helicopter is an aircraft
which is lifted by rotating horizontal rotor blades and is used mainly
for short distance transportation.
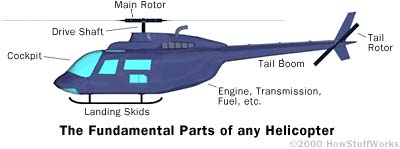 Helicopters consist of several parts which are dependant on the
size and the provided function of the helicopter. The
fundamental parts are the fuselage (body), the main rotor (very
top), small rotor
(near tail), drive shaft (supports main rotor), cockpit, engine,
transmission, fuel and the landing skids. Rotor blades which
are thin and shaped like an aeroplane's wing, keep the craft in
the air. The cockpit (inner cabin), has several components such
as the instrument console, cyclic pitch stick, collective pitch
lever, throttle, rudder pedals, and the pilot's seat. Helicopters consist of several parts which are dependant on the
size and the provided function of the helicopter. The
fundamental parts are the fuselage (body), the main rotor (very
top), small rotor
(near tail), drive shaft (supports main rotor), cockpit, engine,
transmission, fuel and the landing skids. Rotor blades which
are thin and shaped like an aeroplane's wing, keep the craft in
the air. The cockpit (inner cabin), has several components such
as the instrument console, cyclic pitch stick, collective pitch
lever, throttle, rudder pedals, and the pilot's seat.
 Helicopters
do not need a runway, this enables a helicopter to take-off
on just about any surface. The process of take-off begins when
the rotor blades
spin fast and the air force underneath increases to a stage
where it is able to overcome the weight of the craft.
Helicopters can take-off vertically and travel
in any desired direction whether forwards, backwards, left or
right.
While taking-off on land, the pilot controls the helicopter with
one hand grasping the cyclic control, which controls the lateral
direction of the helicopter, whether going forwards, backwards,
left and right. The other hand controls the collective pitch
lever. This controls the up and down motion and the engine speed
of the helicopter. The pilot controls the tail rotor by
compressing his or her feet on the pedals. This allows the
helicopter to rotate in either direction on its axis. Helicopters
do not need a runway, this enables a helicopter to take-off
on just about any surface. The process of take-off begins when
the rotor blades
spin fast and the air force underneath increases to a stage
where it is able to overcome the weight of the craft.
Helicopters can take-off vertically and travel
in any desired direction whether forwards, backwards, left or
right.
While taking-off on land, the pilot controls the helicopter with
one hand grasping the cyclic control, which controls the lateral
direction of the helicopter, whether going forwards, backwards,
left and right. The other hand controls the collective pitch
lever. This controls the up and down motion and the engine speed
of the helicopter. The pilot controls the tail rotor by
compressing his or her feet on the pedals. This allows the
helicopter to rotate in either direction on its axis.
A helicopter flies by
replacing the wings of an aeroplane with a set of rotating
blades. When airborne, the rotors generate lift in the same way
as fixed wings do. The pilot can control the helicopter and
direct it in almost any direction. Unlike an aeroplane, a
helicopter has the ability to fly backwards as well as forwards,
left and right. Helicopters also have the ability to hover
motionless in the air. Rotors come into play in this area by
enabling the helicopter to move forward. The engine provides
lift and horizontal movement. If helicopters didn't have a small
rotor on the fuselage, they would spin around in circles.
Descent is controlled by the speed of the
rotor.
Helicopters
land by reducing the speed
of both the main and
small rotor.
The
fact that a helicopter
can take-off
vertically enables this
amazing aircraft to land in a restricted space.
If you
think about it, a helicopter does not work as simply as it seems. There
is a lot that comes into play with this unique device.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
http://www.amenco.com/freestuff/freesounds/effects.html
www.factmonster.com/ce6/sci/A0823250.html
http://www.howstuffworks.com/helicopters1.htm
http://www.howstuffworks.com/helicopters3.htm
FUNK & WAGNALLS, INC., NEW
YORK
Parsons, A. (1992) What's
Inside Planes? London: Dorling Kindersley Limited
Robins, J. (1986) The
Story Of Flight. New York: Warwick Press
Williams, J.(1991) Flight.
Hove: Wayland
Microsoft Encarta
Encyclopedia Deluxe 2001
| Learning
Process & Self Evaluation: |
| Steps I went
through to create this explanation: |
- Gathered
information from a variety of resources.
- Draft the
explanation.
- Set it
out on the computer.
|
| I have learnt: |
|
| I am good at: |
- Gathering
a variety of useful sources.
|
| I need to work
more on: |
- Writing a
better explanation.
|
| My
effort for this task has been: |
Quality |
My
best work |
Could
do better |
| |
ü |
|
| Comment:
I do not think this is my best work. I did try
my hardest but I do not quite understand how to write an
explanation that well using time words and the needed criteria. |
|
| Teacher
Evaluation: |
| Indicator |
Progressing
Towards |
Achieved |
Working
Beyond |
| Locating
Information |
|
|
|
| Records information
from a variety of sources |
|
|
ü |
| Information is
written in 'own words' |
|
|
ü |
| Information is
detailed and at an appropriate stage level |
|
|
ü |
| Explanation Structure |
|
|
|
| Text explains why
things are as they are or how things work |
|
|
ü |
| Text is consistent
with what the student was asked to explain |
|
|
ü |
| Text begins with a
general statement which defines or describes the phenomena being
explained |
|
|
ü |
| The sequence of
events involves more than one step which explains how the
phenomena occurs |
|
|
ü |
| Uses cause-effect
relationships |
|
|
ü |
| Text contains
technical or subject specific vocabulary |
|
|
ü |
| Text is organised
into paragraphs to signal different stages of explanation |
|
|
ü |
| Includes a correctly
set out bibliography |
|
|
ü |
| Grammar |
|
|
|
| Writes in timeless
present tense |
|
|
ü |
| Sentences are
correctly structured and there is subject/verb agreement |
|
|
ü |
| Writes simple and complex
sentences |
|
|
ü |
| Uses a variety of
conjunctions and connectives |
|
|
ü |
| Uses correct
punctuation |
|
|
ü |
| Spells needed words
correctly (has used Spell Check) |
|
|
ü |
| Presentation |
|
|
|
| Uses accepted typing
conventions |
|
|
ü |
| Uses a variety of
print and script styles for effect |
|
|
ü |
| Includes graphics |
|
|
ü |
| Effective, easy to
read layout |
|
|
ü |
| Comment:
Mariam, you have written a very good
explanation. It is clearly set out, informative and easy to read.
Well done.
Miss Best |
|
|